Administration
Administration tool is available only on Premium edition. In Community edition, please use configuration using environment variables
Administration tool is still in development, so there could be some backward incompatible changes till September release.
Administration page is available on URL https://your_dbgate_instance/admin.html . You have to set environment variable ADMIN_PASSWORD to enable this administration. You could then add administration permission to different user with different authentication method, but at first, you have to open this admin page.
All configuration from administration is saved into database, use STORAGE_xxx environment variables for configure this.
Authentication tab
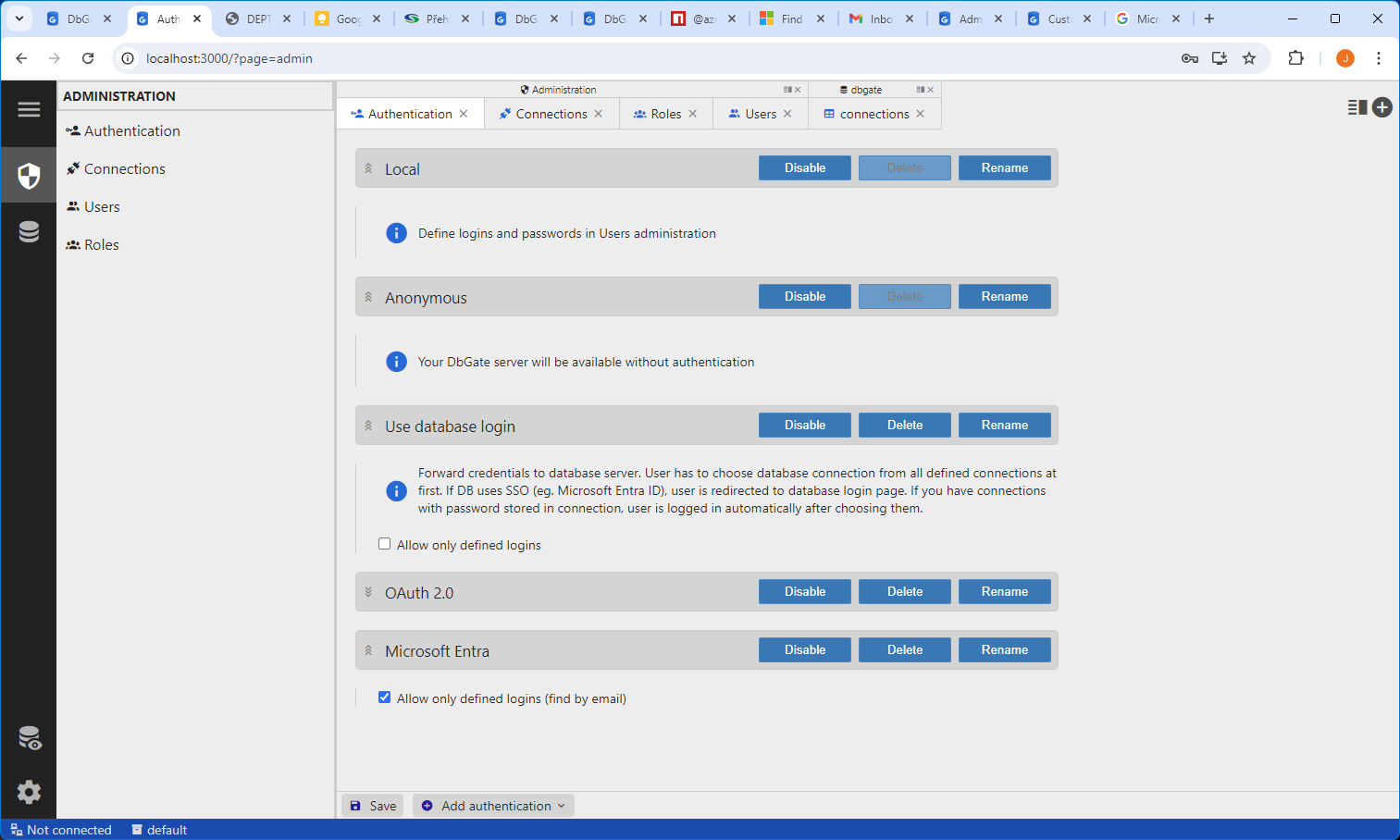
There are several methods of authentication. Use will choose authentication method on login page. If you have only one authentication method enabled and authentication method doesn’t require login page, login page is skipped.
- Local authentication method - user is selected from user list in storage database (configured in “Users” tab)
- Anonymous - no credentials are required, user have permissions from “anonymous-user” role
- Use database login - credentials are redirected to database server. User will choose connection from “Connections” tab
- OAuth 2.0 - generic OAuth provider. With some little effort and proper knowledge, could be configured with most of recent identity providers, like Google, Facebook, Keycloak
- Active Directory - AD access via LDAP protocol
- Microsoft Entra - former Azure Active Directory - single sign-on access to Azure databases
Option “Allow only defined logins”
For external identity providers, user doesn’t have to exist in DbGate storage database. If this checkbox is checked, user, which is not found in storage database, is not allowed to login
Connections tab
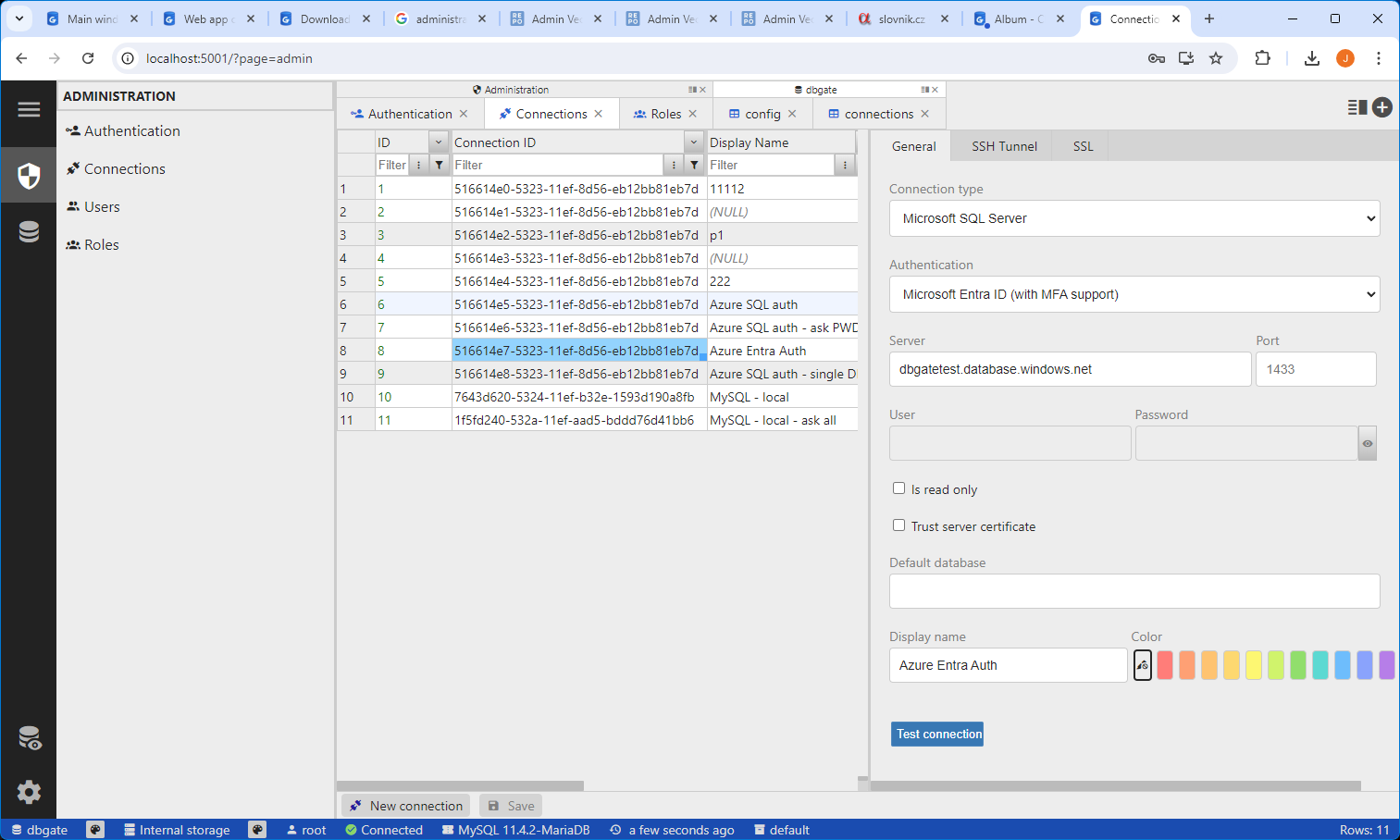
Configure connections available in DbGate. Connections must be mapped to users and roles to be available.
Users tab
Configure users, passwords, user permissions and user-connection mapping. Passwords are used only for “Local” authentication methods. But all methods with external identity providers use user lookup, so you could configure permissions and connections available for user, even for externaly authenticated user.
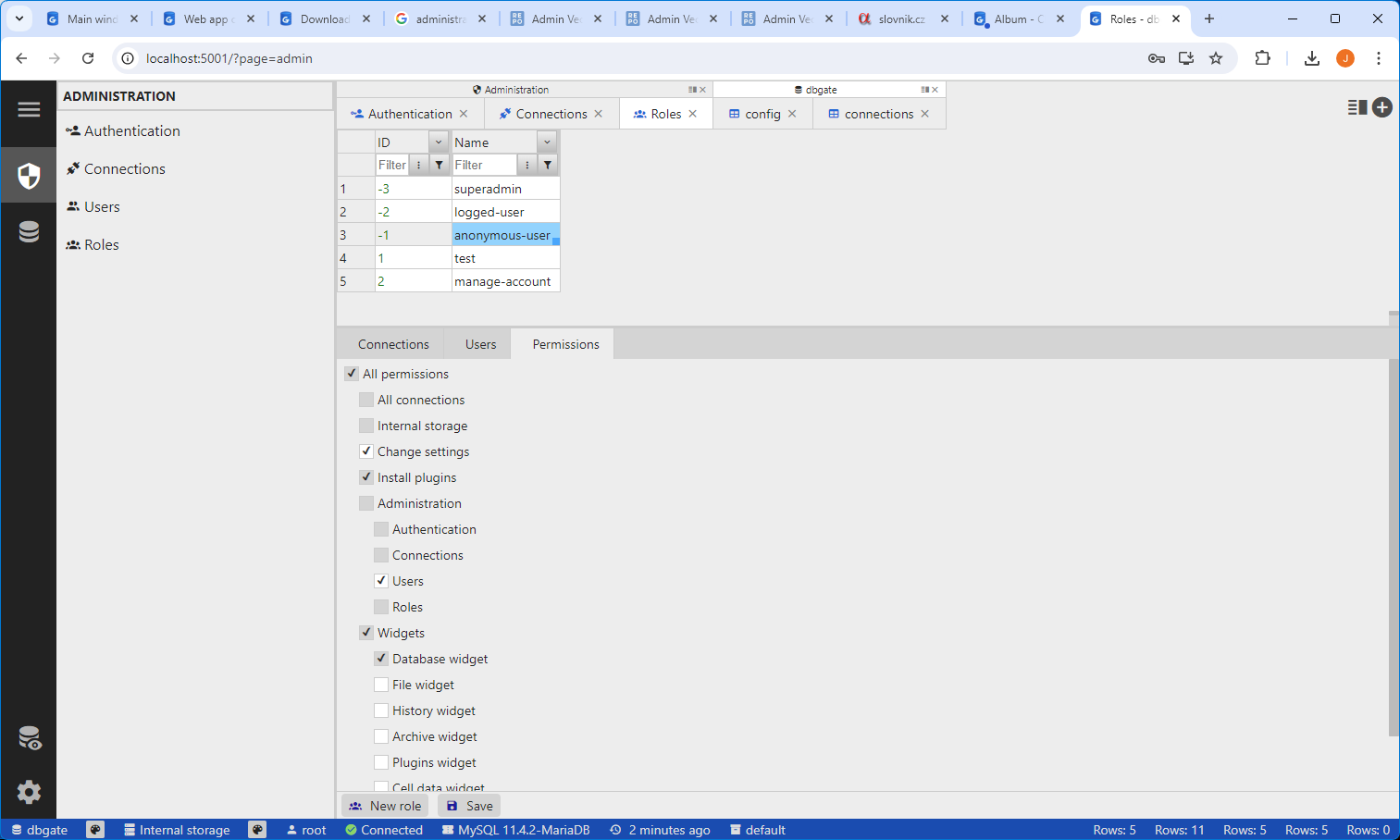
Roles tab
Configure roles, role permissions and role-connection mapping. You could create custom roles and assign users to them, so that permissions and linked connections are shared between all users assigned to this role.
There are some predefined roles:
- superadmin - role used for admin page, https://your_dbgate_instance/admin.html
- logged-user - role used for all logged users. You could ovveride permission for specific users
- anonymous-user - role used for users logged with “Anonymous” authentication method
Direct access to storage database
Admin user has also access to internal storage database, so you could make operations on database directly (eg. exports/imports of users etc.). This permission could be also granted to any other user, “Interal storage” permission
Permissions system
DbGate uses permission system with two dimensional hiearchy.
One hiearchy dimension is inheritance of permissions from roles.
- Predefined permission set
- Predefined role (superadmin/logged-user/anonymous user)
- Custom roles
- User
The second hiearchy dimension is inheritance from parent roles.
Coul can see permission tree on following screenshot: